Asymmetric route
Summary
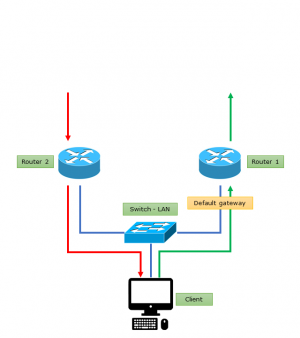
Assimetric route is formed typically, when in a network more router works. These can be in HA mode or connect different networks. We are talking about an asymmetric route if an host start a session via one router - typically via default router - , but the answer arrive via the other router.
There is no problem in WAN environment, in fact this is an advantage, because the one of base feature of IP network that there are several route between A and B point, what the routers choose dynamically.
In LAN environment the problem is that on L2 the answer arrives from other mac address, the communication was heading for. The man in the middle attack may cause this anyway, therefore the devices and protocols do not support the asymmetric route. Furthermore the asymmetric route sensitivity of an device depend on level of IP stack implementation too.
In a route table of a device can be only one (active) default route, therefore to avoid the problems and anomalies caused by asymmetric route the network topology must be logically and / or physically organized to the all network and services can be accessible via one default gateway.
The below article shows cases of the asymmetric route and possible methods of avoidance.
Multiple gateways
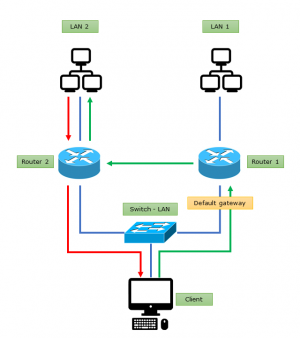
In this case difference networks are available behind the routers.
The asymmetric route can be eliminated with next methods in such a case.
Static route
There is possibility set static route in operating systems next to default gateway. In the example the default route is the 1. router, and we set a static route to 2. router. So the current host will know some networks need to send packets in a different direction than the default gateway.
Add static route in Windows:
route -p add 192.168.2.0 MASK 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.2
Add static route in linux:
route add -net 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.0.2 dev eth0
or
ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 via 192.168.0.2 dev eth0
The disadvantage of this method is obvious, in many host case there are many manually setting and if the network configuration is changed we have to also follow manually the changes. Only in few hosts case worth use this, for example one server must be accessible from the network behind router 2.
Distribute static route with DHCP[1]
The essence of the method is the same like at the static route with the difference that the hosts get the the static route over DHCP. So the configuration becomes simple and flexible.
The 33 (host), 121 (network) and 249 (Microsoft)options of DHCP provide the static routes, however the host can understand these are already a matter of DHCP client implementation. The IP devices with higher level typically operate (e.g. operating systems), but the simpler ones not necessarily (e.g. printers). Therefore if our all devices have to communicate with the network 2. then this method is not appropriate either.
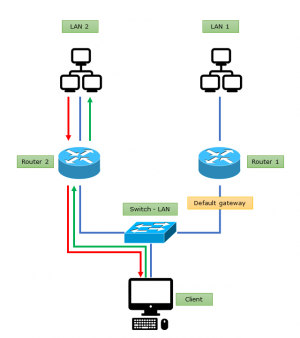
Policy based routing [2]
All you have to do is change the network topology.
There is a static route to router 2. in router 1. It is given, because also required to create an asymmetric route.
A 2. routernek viszont megmondjuk, hogy minden esetben az 1. routernek küldje a tárgyi hálózatba irányuló forgalmat, annak ellenére, hogy az eszköznek van interfésze (connected route) ebben a hálózatban. Ez ellenkezik az alap routing logikával, ezét kell felvenni rá egy szabályt.
Hogy egy router milyen beállításokkal képes ilyen működésre, illetve hogy képes e, az gyártó és típus kérdése, új eszköz integráció előtt mindenképpen tájékozódni kell róla.
Hátránya, hogy minden kereszt-hálózati forgalom (LAN 1 <-> LAN 2) megjelenik a LAN hálózatban. Sok hálózat összekötésére nem alkalmas. Jellemzően kényszerűségből választják ezt a módszert, ha valamely okból az egyéb megoldások nem használhatóak.
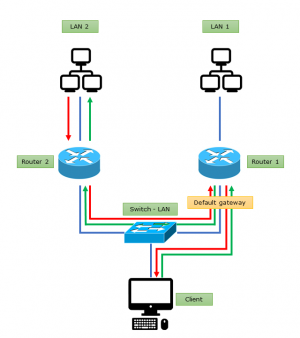
Helyes L3 topológia
bélyegkép|Right topology, one gateway in a networkA végső megoldás az, ha úgy szervezzük a hálózatot, hogy valóban csak egy átjáró (router) legyen egy alhálózatban. Az alhálózatok routerekkel, a routerek pedig dedikált interfészekkel és technikai alhálózatokkal kommunikáljanak egymással. Mindig erre kell törekedni, amennyiben nincs kizáró ok.
HA[3] router
bélyegkép|HA routers Ekkor a router-ek mögött ugyanazok a hálózatok érhetőek el. (vagy különbözőek, de ugyanaz a céljuk. pl.: redundáns ISP) Ez esetben azért helyezünk két routert a hálózatba, mert azt szeretnénk, hogy ha az egyik meghibásodik vagy egyéb más ok miatt nem tudja ellátni a feladatát, akkor a másik végezze el azt.
Egy alhálózatban nem lehet két eszköznek ugyanaz az IP címe. Tehát a két routernek különböző IP címe lesz, amiből csak az egyik lehet az alapértelmezett átjáró. Ezért HA átálláskor, ha a passzív router még elérhető a kliensek számára, akkor létrejön az aszimmetrikus route, ha pedig nem elérhető, akkor hiába működik a másik, a kliensek erről nem tudnak, így funkcionálisan nem fog működni a HA router cluster.
A megoldás valamely FHRP[4] protokoll, amit arra fejlesztettek ki, hogy két eszköz eldöntse éppen melyik használjon egy közös IP címet. Ha az egyik kiesik, a másik automatikusan felveszi azt, és folytatja a munkát vele.
A kliensek L2 szinten ARP[5] protokollon értesülnek a változásról, L3 szinten (számukra) nem történik változás a hálózatban.
Hogy a router milyen FHRP protokollt támogat, illetve hogy támogat e, az szintén gyártó és típus függő.